Beyond Moore-Penrose Part II: The Sparse Pseudoinverse
Résumé
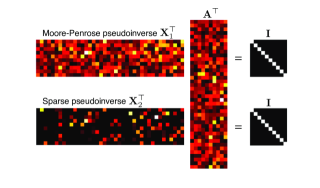
This is the second part of a two-paper series on generalized inverses that minimize matrix norms. In Part II we focus on generalized inverses that are minimizers of entrywise p norms whose main representative is the sparse pseudoinverse for $p = 1$. We are motivated by the idea to replace the Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse by a sparser generalized inverse which is in some sense well-behaved. Sparsity implies that it is faster to apply the resulting matrix; well-behavedness would imply that we do not lose much in stability with respect to the least-squares performance of the MPP. We first address questions of uniqueness and non-zero count of (putative) sparse pseu-doinverses. We show that a sparse pseudoinverse is generically unique, and that it indeed reaches optimal sparsity for almost all matrices. We then turn to proving our main stability result: finite-size concentration bounds for the Frobenius norm of p-minimal inverses for $1 ≤ p ≤ 2$. Our proof is based on tools from convex analysis and random matrix theory, in particular the recently developed convex Gaussian min-max theorem. Along the way we prove several results about sparse representations and convex programming that were known folklore, but of which we could find no proof.
Fichier principal
 pseudo-part2.pdf (714.09 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
pseudo-part2.pdf (714.09 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 spinv_illustration.pdf (913.52 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
spinv_illustration.pdf (913.52 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |