Computation and Visualization of Risk Assessment in Deep Brain Stimulation
Résumé
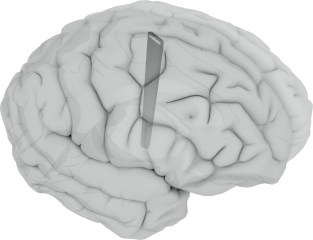
Deep Brain Stimulation is a neurosurgical approach for the treatment of pathologies such as Parkinson's disease. The basic principle consists in placing a thin electrode in a deep part of the brain. To safely reach the target of interest, careful planning must be performed to ensure that no vital structure (e.g. blood vessel) will be damaged during the insertion of the electrode. Currently this planning phase is done without considering the brain shift, which occurs during the surgery once the skull is open, leading to increased risks of complications. In this paper, we propose a method to compute the motion of anatomical structures induced by the brain shift. This computation is based on a biomechanical model of the brain and the cerebro-spinal fluid. We then visualize in a intuitive way the risk of damaging vital structures with the electrode.
La stimulation cérébrale profonde est une procédure neurochirurgicale pour le traitement de pathologies comme la maladie de Parkinson. La procédure consiste à implanter une électrode dans une région profonde du cerveau. Pour atteindre la cible sans risque, le chirurgien procède à une plannification minutieuse pour s'assurer qu'aucune structure vitale (vaisseaux sanguins, ventricules) ne se retrouve sur le chemin de l'électrode. Actuellement, la plannification ne considère pas les déformations intra-opératoires, qui se produisent une fois que le crâne est ouvert. Cela peut entraîner des compolications. Dans ce papier, nous proposons une méthode pour calculer le risque de mouvement des structures anatomiques causés par ces déformations. Le calcul s'appuie sur un modèle biomécanique du cerveau et du fluide céphalo-rachidien. Nous visualisons ensuite intuitivement le risque d'endommager une structure vitale avec l'électrode.
Domaines
Modélisation et simulation
Fichier principal
 Bilger_A.pdf (1.27 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
Bilger_A.pdf (1.27 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 rendu5.png (836.66 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
rendu5.png (836.66 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|