From Video Matching to Video Grounding
Résumé
This paper addresses the background estimation problem for videos captured by moving cameras, referred to as video grounding. It essentially aims at reconstructing a video, as if it would be without foreground objects, e.g. cars or people. What differentiates video grounding from known background estimation methods is that the camera follows unconstrained motion so that background undergoes ongoing changes. We build on video matching aspects since more videos contribute to the reconstruction. Without loss of generality, we investigate a challenging case where videos are recorded by in-vehicle cameras that follow the same road. Other than video synchronization and spatiotemporal alignment, we focus on the background reconstruction by exploiting inter- and intra-sequence similarities. In this context, we propose a Markov random field formulation that integrates the temporal coherence of videos while it exploits the decisions of a support vector machine classifier about the backgroundness of regions in video frames. Experiments with real sequences recorded by moving vehicles verify the potential of the video grounding algorithm against state-of-art baselines.
Fichier principal
 ICCVW-CVVT-2013.pdf (8.82 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
ICCVW-CVVT-2013.pdf (8.82 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
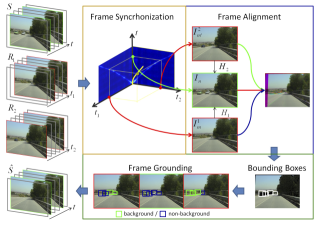 videoGrounding.png (1.57 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
videoGrounding.png (1.57 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
Loading...