Plaquage omnidirectionnel de textures provenant de séquences vidéo
Résumé
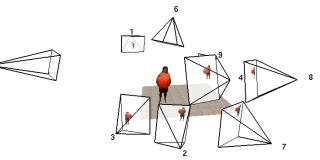
In video-based rendering, real dynamic scenes are captured by video cameras and replayed, so that they can be seen by the observer from any viewpoint. In order to permit a complete immersion of the real scene in a virtual environment, some approaches reconstruct a 3D shape and then textured it with images taken from the cameras.
This paper proposes to identify the problems of multi-view texturing for video-based rendering and to offer solutions for a number of them.We successfully treat visibility issues, identify "risk zones", correct projection displacement errors and fill in small untextured areas. Our algorithm works in real time, thus permitting an interactive viewing of the augmented scene
This paper proposes to identify the problems of multi-view texturing for video-based rendering and to offer solutions for a number of them.We successfully treat visibility issues, identify "risk zones", correct projection displacement errors and fill in small untextured areas. Our algorithm works in real time, thus permitting an interactive viewing of the augmented scene
Nous proposons dans cet article d'identifier clairement les problèmes rencontrés lorsque l'on veut effectuer un texturage omnidirectionnel d'un modèle 3D. Nous proposons aussi des solutions à chacun de ces problèmes. Une version anglaise, plus détaillée, se trouve en deuxième partie.
Fichier principal
 orzan_afig_2006.pdf (1.09 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
orzan_afig_2006.pdf (1.09 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 cube_simple.jpg (98.02 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
cube_simple.jpg (98.02 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 cameras.gif (37.33 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
cameras.gif (37.33 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 cube_us.jpg (95.86 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
cube_us.jpg (95.86 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
| Format | Figure, Image |
|---|
Loading...