Hexahedral Meshing: Mind the Gap!
Résumé
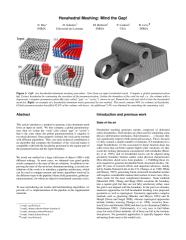
This article introduces a method to generate a hex-dominant mesh from an input tet mesh. We first compute a global parameterization, then we isolate the ``void'' (also called ``gap'' or ``cavity''), that is the zone where the global parameterization is singular or too much distorted. Once properly isolated, the void can be meshed with different algorithms. Thus, our main technical contribution is an algorithm that computes the boundary of the void and makes it compatible with both the hexahedra generated in the regular part of the parameterization and the input boundary. We tested our method on a large collection of objects (200+) with different settings. In most cases, we obtained very good quality results compared to the state-of-the-art solutions. In addition to improving the state-of-the-art in hex-dominant meshing, a second contribution of this work is to introduce a pipeline architecture, which can be used to compare present and future algorithms involved in the different steps of the pipeline (frame field generation, global parameterization), for which no objective benchmark currently exists. To ease reproducing our results and benchmarking algorithms, we provide a C++ implementation of the pipeline in the supplemental materials.
Domaines
Géométrie algorithmique [cs.CG]
Fichier principal
 hexdom_current.pdf (10.3 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
nbtets_report_4_1_2017_bis.pdf (602.75 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
hexdom_current.pdf (10.3 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
nbtets_report_4_1_2017_bis.pdf (602.75 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers éditeurs autorisés sur une archive ouverte |
|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|